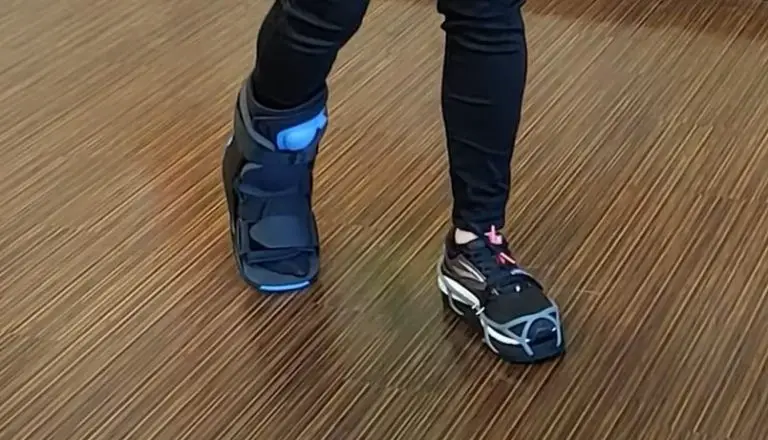
How Does a Walking Boot Work?
Injuries to the foot or ankle can significantly impact mobility and hinder daily activities. To aid in the healing process and provide support, medical professionals often recommend the use of a walking boot.
This article aims to explore the inner workings of a walking boot, shedding light on its components, functionality, proper usage, and care instructions.
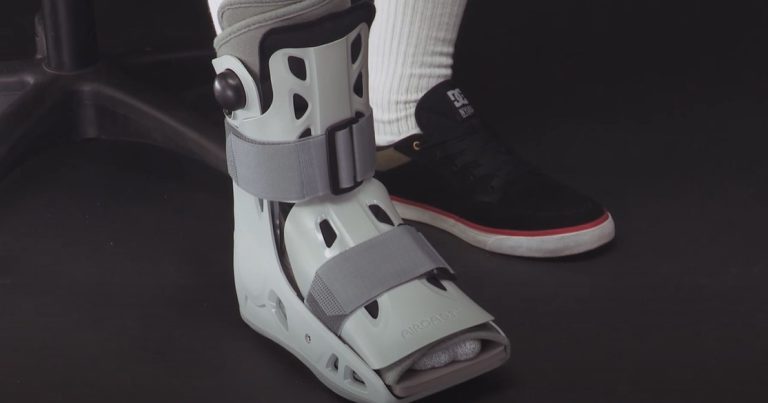
Components of a Walking Boot
A walking boot comprises several key components that work together to provide stability, support, and comfort.
- Sole: The sole of a walking boot features a carefully designed tread pattern and grip to enhance traction. It also incorporates shock absorption features, reducing the impact on the injured foot or ankle.
- Upper: The upper part of the walking boot is constructed using durable materials. It may feature various fastening mechanisms such as straps, zippers, or laces to secure the boot in place.
- Support Structures: Metal or plastic reinforcements within the walking boot provide structural support. These components can be adjusted to achieve a personalized fit, accommodating variations in foot shape and swelling.
- Padding and Cushioning: Walking boots are equipped with inner padding and cushioning materials. These serve two purposes: absorbing impact during movement and distributing pressure evenly across the foot and ankle.
The functionality of a Walking Boot
Walking boots offer several essential functions that aid in the healing process and facilitate mobility.
Immobilization and Protection: The primary function of a walking boot is to immobilize and protect the injured area. By stabilizing the foot and ankle, the boot minimizes excessive movement, reducing the risk of further injury.
Weight-Bearing Support: Walking boots are designed to offload pressure from the injured foot or ankle, allowing for weight-bearing activities. This support promotes healing and facilitates a quicker recovery.
Alignment and Gait Correction: A walking boot helps maintain proper alignment of the foot and ankle. By preventing misalignment, it promotes a natural gait and aids in the correction of abnormal walking patterns caused by injury.
Gradual Transition: During the healing process, walking boots are used in different phases. Initially, the boot provides maximum support and immobilization. As healing progresses, healthcare professionals guide patients in gradually reducing their reliance on the boot until it is no longer needed.
Proper Usage and Care
To ensure the effectiveness of a walking boot and minimize complications, proper usage and care are crucial.
Fitting and Adjustments:
Correct sizing and adjustments are essential for optimal comfort and support. Healthcare professionals should guide patients in selecting the appropriate size and demonstrate how to properly place and tension the straps for a secure fit.
Instructions for Walking and Weight-Bearing:
Patients should follow specific instructions provided by their healthcare professionals on walking techniques and weight-bearing limitations.
These guidelines ensure stability and prevent further injury while allowing the gradual strengthening of the affected foot or ankle.
Cleaning and Maintenance:
Regular cleaning and maintenance are necessary to keep the walking boot in good condition. This involves removing and cleaning the inner padding, inspecting the boot for wear and tear, and replacing any components that show signs of damage.
How to use a walking boot?
Using a walking boot correctly is essential for ensuring proper support, protection, and healing of foot or ankle injuries. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use a walking boot effectively:
Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before using a walking boot, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who can assess your injury and provide specific instructions tailored to your condition.
They will guide you on the duration of usage, weight-bearing limitations, and any additional precautions.
Choose the Right Size: Ensure that you have the correct size of walking boots. A proper fit is necessary for optimal support and comfort.
Follow the sizing guidelines provided by the manufacturer or seek guidance from a healthcare professional.
Prepare the Boot: Before putting on the walking boot, ensure that all straps, laces, or fastening mechanisms are loosened and fully open. This will make it easier to slide your foot into the boot.
Positioning the Foot: Carefully place your injured foot into the walking boot, ensuring that your heel is all the way back against the back of the boot.
Make sure your toes are properly aligned with the footbed. If there are any adjustable support structures, adjust them as directed by your healthcare professional to achieve a snug and secure fit.
Fasten the Straps: Begin fastening the straps or other closures in the order recommended by your healthcare professional.
Start from the lower part of the boot and work your way up. Secure the straps firmly but not too tight, ensuring they are snug enough to hold your foot in place.
Check for Proper Fit: Once all the straps are fastened, check the fit of the walking boot.
It should feel snug but not excessively tight, allowing for some movement of the toes. Avoid over-tightening the straps as it may restrict circulation or cause discomfort.
Follow Weight-Bearing Instructions: Adhere to the weight-bearing instructions provided by your healthcare professional.
They may recommend partial weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing depending on the nature and severity of your injury. Use crutches or other assistive devices as necessary to ensure proper weight distribution.
Walking Technique: When walking with a walking boot, maintain an even gait and take slow, deliberate steps.
Focus on using the muscles and joints of the uninjured leg to assist in movement. Avoid putting excessive pressure or impact on the injured foot or ankle.
Follow Care Instructions: Proper care of the walking boot is essential for maintaining its effectiveness and hygiene.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cleaning and maintaining the boot. This may involve removing and cleaning the inner padding, inspecting for wear and tear, and replacing any damaged or worn-out components.
Follow Up with Healthcare Professional: Regularly schedule follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional to monitor your progress and receive guidance on transitioning out of the walking boot.
They will provide instructions on gradually reducing usage and resuming normal activities.
Remember, every injury and treatment plan is unique, so it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance on using a walking boot effectively.
Advantages and Limitations
Understanding the advantages and limitations of a walking boot can help individuals make informed decisions about their usage.
Advantages of Using a Walking Boot: Walking boots offer significant advantages, including protection and support for injured foot or ankle, improved mobility compared to casts or crutches, and the ability to gradually increase weight-bearing activities as the healing progresses.
Limitations and Potential Drawbacks: While walking boots are effective in their intended purpose, they do have limitations. Restricted range of motion is one drawback, as the boot immobilizes the foot and ankle.
Prolonged use may also lead to discomfort or skin irritation, necessitating proper care and periodic breaks from wearing the boot.
FAQs
How long do I need to wear a walking boot?
The duration of walking boot usage varies depending on the type and severity of the injury. Your healthcare professional will provide specific instructions based on your condition. It can range from a few weeks to several months.
Can I remove the walking boot while resting or sleeping?
Unless advised otherwise by your healthcare professional, it is generally recommended to keep the walking boot on during rest and sleep. The boot provides stability and protection to the injured foot or ankle, promoting healing and preventing further injury.
Can I drive while wearing a walking boot?
Driving with a walking boot is not recommended for safety reasons. The bulkiness and limited range of motion may affect your ability to operate the vehicle safely. Consult with your healthcare professional for guidance on driving restrictions during your recovery period.
Can I shower or bathe with a walking boot on?
In most cases, walking boots are not waterproof, and getting them wet can affect their integrity and comfort. Your healthcare professional may provide specific instructions, such as using a waterproof cover or removing the boot temporarily while bathing. Follow their recommendations to protect the boot and prevent complications.
Can I engage in physical activities or exercise while wearing a walking boot?
Engaging in physical activities or exercise while wearing a walking boot should be discussed with your healthcare professional. Depending on your injury, they may advise certain activities that are safe and beneficial. However, high-impact or strenuous activities are usually restricted while wearing a walking boot.
What should I do if the walking boot causes discomfort or skin irritation?
If you experience discomfort or skin irritation while wearing the walking boot, it is important to address it promptly. Ensure that the boot is properly fitted and not overly tightened. If the discomfort persists or worsens, contact your healthcare professional for further evaluation and potential adjustments to the boot or alternative solutions.
Conclusion
Walking boots play a vital role in supporting the healing process of foot and ankle injuries. By providing immobilization, protection, weight-bearing support, and gait correction, these boots offer a safe and efficient means of recovery.
Adhering to proper usage and care instructions, as well as following the guidance of healthcare professionals, will maximize the benefits of a walking boot and help individuals regain their mobility and return to their daily activities sooner.